constraints
knowing what to do
types of constraints
physical
cultural
semantic
logical
physical
physical limitations
constrain possible operations through physical properties
best when restricting before interaction
orientation
directional movement

advantages of physical constraints
rely upon properties of physical world
no special training
encourage desired actions by limiting others
cultural
cultural constraints
cultural norms: allowable actions for social situations
shared by a group
learned
not universal, change with time
can make errors
twitch chat

what do you do when using something new?
youtube tutorials

mac help menu
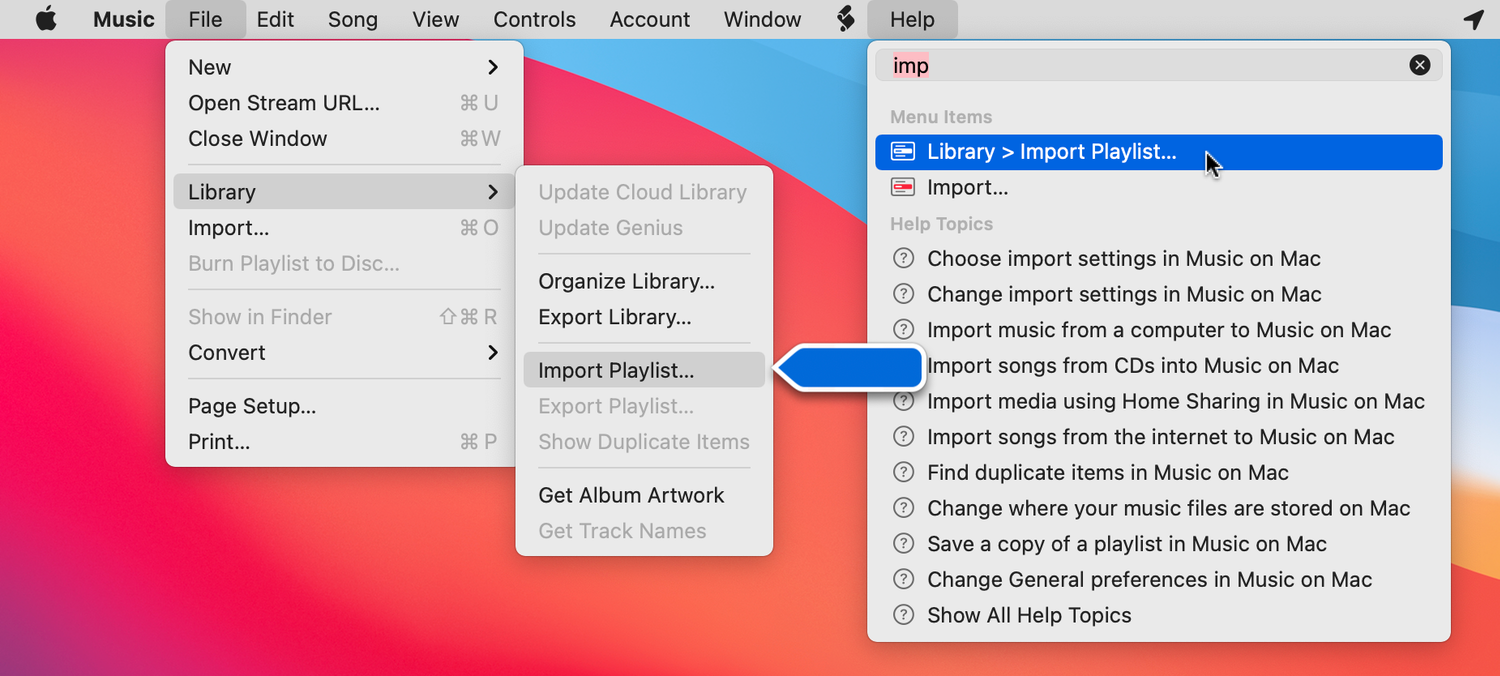
semantic
semantic constraints
rely upon meaning of the situation
rely upon knowledge of the world
learned, not universal
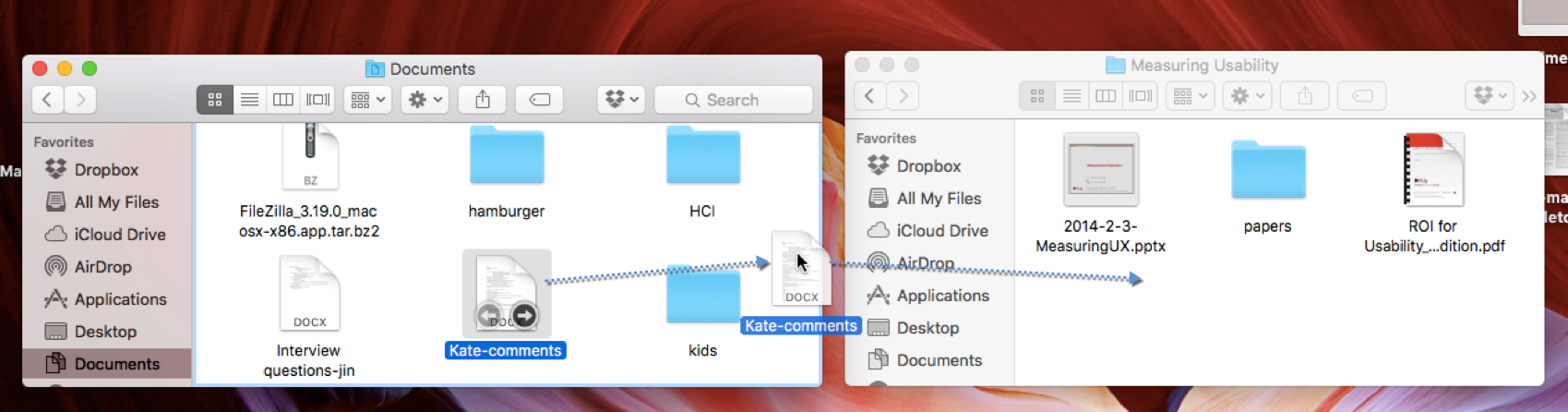
logical
logical constraints
reasonable understanding of how something works
trial and error
conventions and standards
conventions
cultural constraints
inform how people should behave in (social) interactions
conflicts disrupt interaction
chat interfaces

coding conventions

changes in conventions
difficult to change
users object and complain
requires new learning
benefits need to outweigh costs
windows 7 start menu
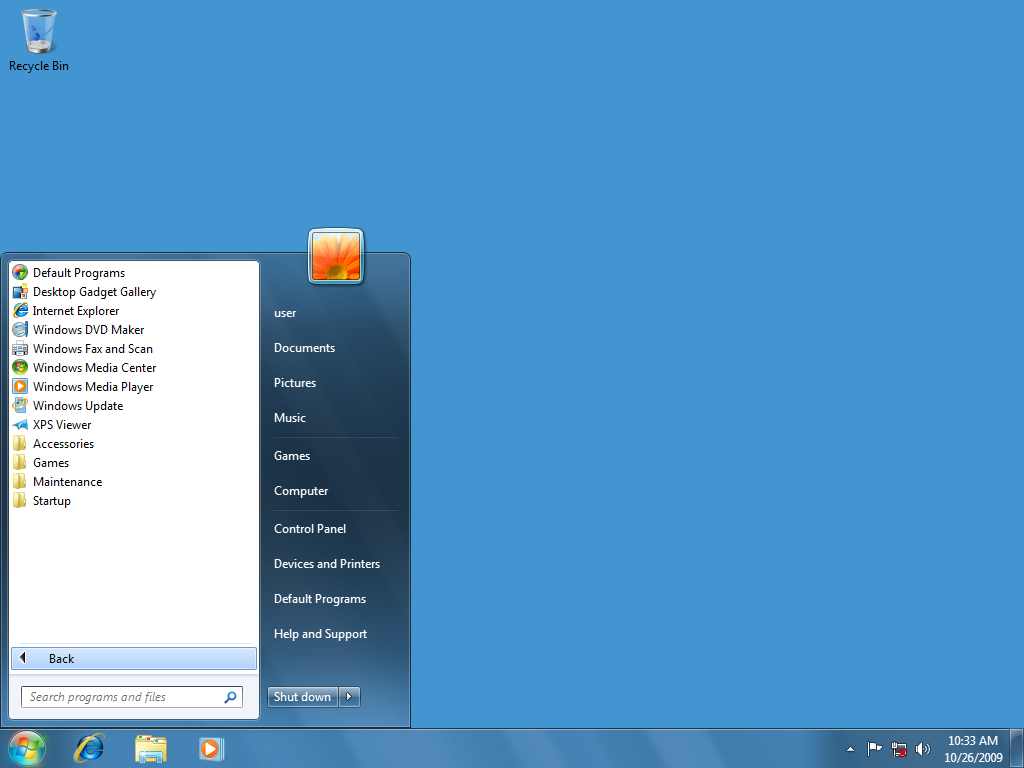
windows 8 start menu
windows 10 start menu
experiences with changes?
constraints and forcing behavior
forcing functions
form of physical constraint
failure at one stage prevents next steps
strong constraint to prevent behaviors
lock-ins
keep an operation active
prevent prematurely stopping
dialog boxes
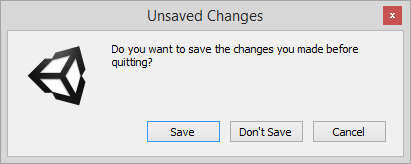
modal toolbars

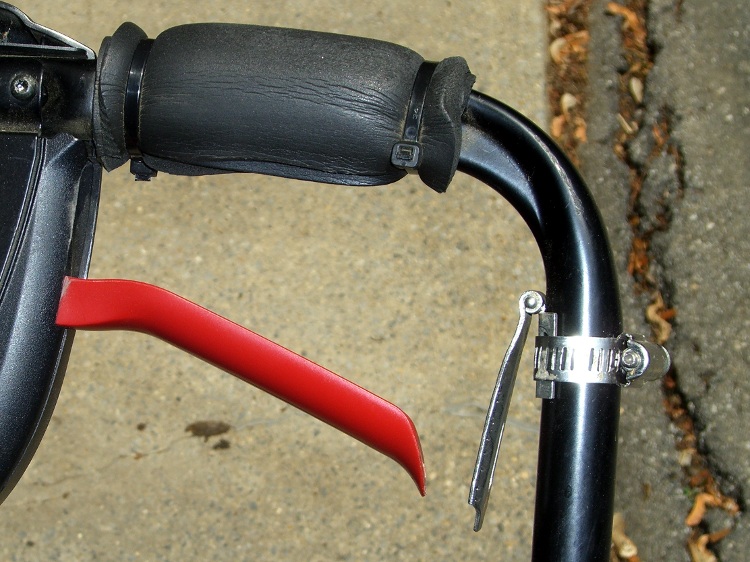
lockouts
prevent an event from occurring
used for safety reasons
can be nuisance
minimize nuisance, maintain safety
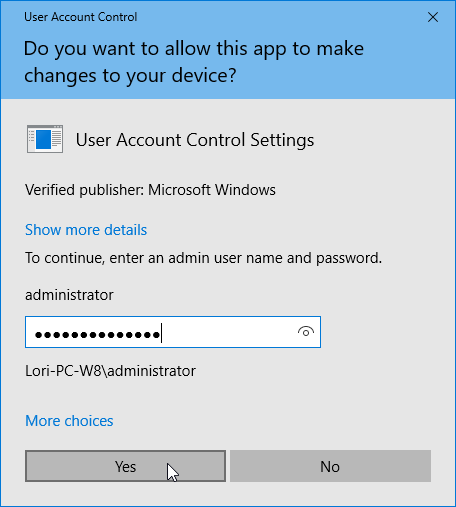
interlocks
force the proper sequence

questions?
reading for next class
Chapter 2: Process of Interaction Design
Interaction Design

Chapter 6:Design Thinking
The Design of Everyday Things
