prototyping and design
what is a prototype?


prototype
manifestation of design
allows interaction by stakeholders
limited characteristics
many forms: from paper to software
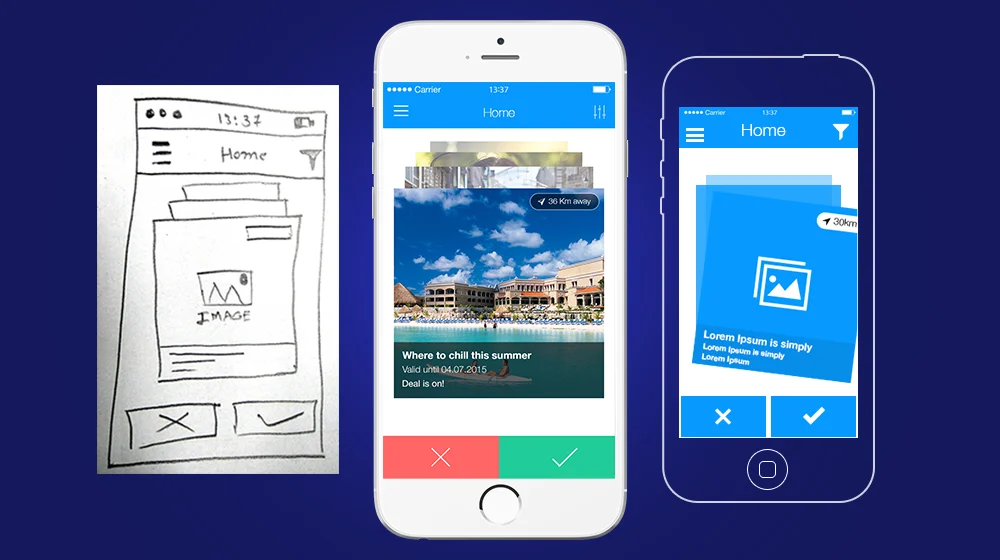
why prototype?
discuss and evaluate ideas
communication device
choosing alternatives
encourage reflection
answer questions
low-fidelity prototyping
low-fidelity prototype
different medium than final product
paper, cardboard, wire frames
limited set of functions
simple, cheap, and quick to produce
modification

storyboarding
series of sketches
show user interaction
used with scenarios
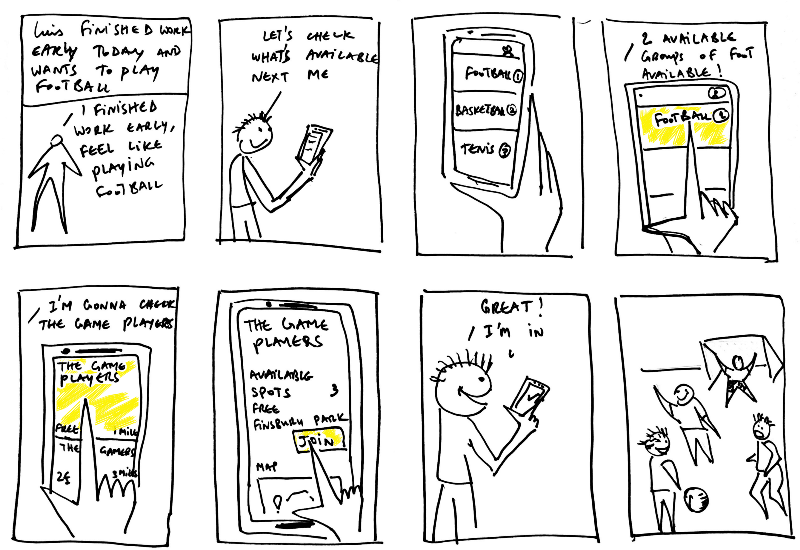
sketches
not about drawing, about design
devise symbols and icons
simple boxes, stick figures, and stars
interfaces: draw icons and dialog boxes
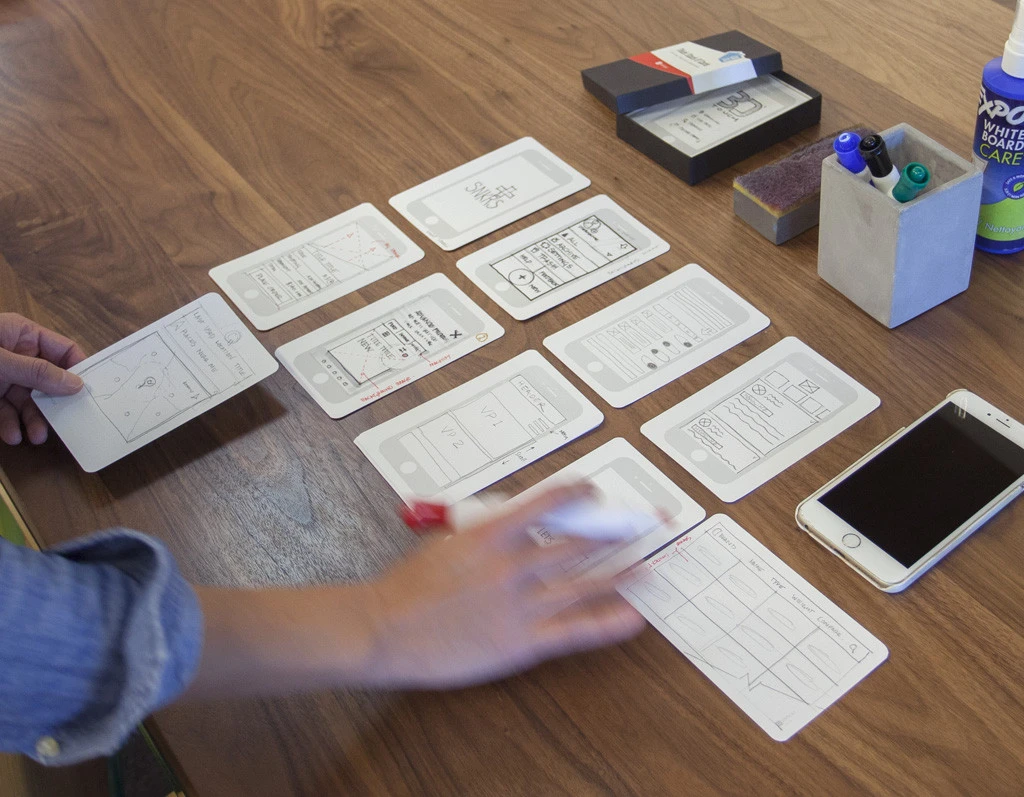
index cards
small pieces of cardboard or thick paper
each card represents one element of the interaction
screen, icon, menu, dialog exchange
evaluation: step through the cards

wizard of oz
software-based prototype
human operator simulates software response
high-fidelity prototyping
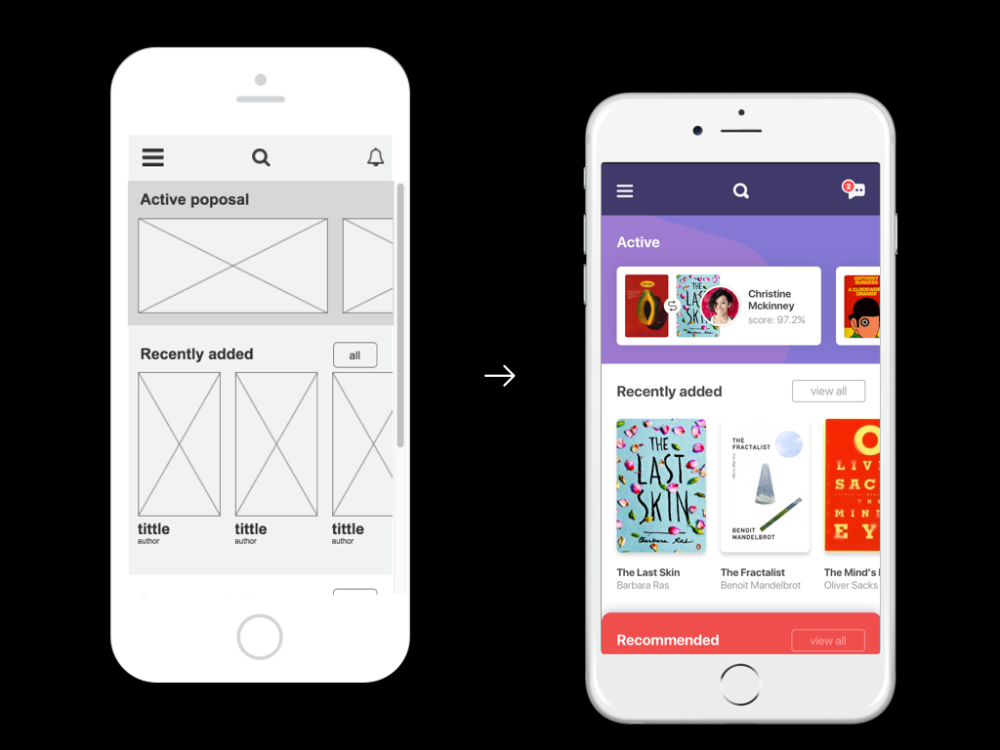
high-fidelity prototype
looks more like final product
provides more functionality
may be used “in the wild”
technology probes
modifying and integrating existing components
compromises
prototypes involve compromises
produce something quickly to test
limited questions can be answered
built with key issues in mind
horizontal and vertical prototyping
horizontal and vertical prototyping
breadth vs depth of functionality
range of functions vs level of detail

consequences of high-fidelity
appear good enough to be final product
users less prepared to critique
fewer alternatives considered
evolutionary vs throwaway prototyping
evolutionary: iteratively develop prototypes towards final product
throwaway: prototypes are stepping stones; final product built from scratch
conceptual design
what is conceptual design?
concerned with developing a conceptual model
conceptual model: outline what users can do and how users learn what they can do
first step: look at data to understand user goals and empathize
contextual interviews
scenarios
initial conceptual model
interface metaphor
interaction types
interface types
interface metaphors
combine familiar knowledge with new knowledge
choosing metaphors: balance utility and relevance
step 1: identify functional requirements
step 2: what is likely to cause user problems
step 3: generate metaphors
evaluating metaphors
does it supply structure?
how much of the metaphors is relevant?
is the metaphor easy to represent?
will your audience understand the metaphor?
how extensible is the metaphor?
example: student course choosing as online shopping
interaction types
instructing, conversing, manipulating, exploring, responding
conceptual models: combination of interaction types
which type is best suited for design?
example: student course choosing as online shopping
interface types
design and practical purpose
avoid influence by a predetermined interface type
different perspectives depending on type
types: graphical, multimedia, web, mobile, gesture, multimodal, shareable, tangible, smart
example: student course choosing as online shopping
concrete design
what is concrete design?
emphasis on concrete detail
producing prototypes
balance range of other requirements with functional requirements
sometimes conflict
aspects of concrete design
visual appearance: graphic design
choice of interaction devices
issues of user characteristics and context
accessibility and inclusiveness
questions?
next class
requirements presentations