low-fidelity prototyping
what is a prototype?


prototype
manifestation of design
allows interaction by stakeholders
limited characteristics
many forms: from paper to software
why prototype?
discuss and evaluate ideas
communication device
choosing alternatives
encourage reflection
answer questions
low-fidelity prototyping
low-fidelity prototype
different medium than final product
paper, cardboard, wire frames
limited set of functions
simple, cheap, and quick to produce
modification

storyboarding
series of sketches
show user interaction
used with scenarios
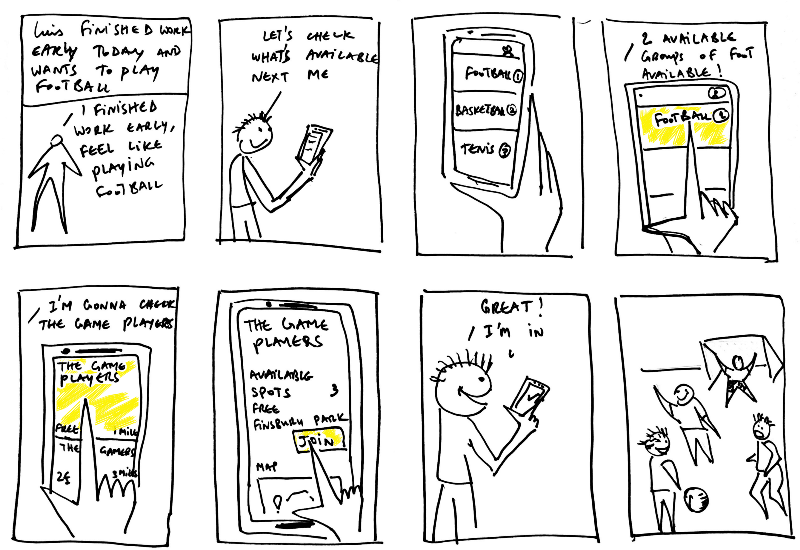
sketches
not about drawing, about design
devise symbols and icons
simple boxes, stick figures, and stars
interfaces: draw icons and dialog boxes
index cards
small pieces of cardboard or thick paper
each card represents one element of the interaction
screen, icon, menu, dialog exchange
evaluation: step through the cards

wizard of oz
software-based prototype
human operator simulates software response
prototyping activity
low-fidelity prototyping activity
low-fidelity prototype a design for
an alarm clock (app or physical device)
come up with a new design: substitute, combine, adapt,
modify (magnify or minify), or eliminate
form pairs
have your partner interact with one or both of your prototypes
ask them questions about their experience
reflection
questions?
reading for next class
Chapter 14: "Introducing Evaluation"
Interaction Design: Beyond Human-Computer Interaction
