what is interaction design?
interaction design
"designing interactive products to support the way people communicate and interact in their everyday and working lives"
[Sharp, Rogers, and Preece 2019]
human-centered approaches
focus on human users and stakeholders
technology supports human activity
design with technology limitations in mind
multidisciplinary
concerns of interaction design
user experience
usability
accessibility and inclusiveness
user experience (UX)
designing for experience
how people feel about a product
macro to micro experiences
goal: "reduce the negative aspects of user experience while enhancing the positive ones"
understanding users
different needs and requirements
no one-size-fits-all
avoid assumptions
cultural differences
user experience goals
desirable: satisfying, enjoyable, fun, helpful, entertaining, aesthetically pleasing, motivating, rewarding, supportive of creativity
undesirable: boring, frustrating, unpleasant, patronizing, annoying, making one feel stupid
course registration system
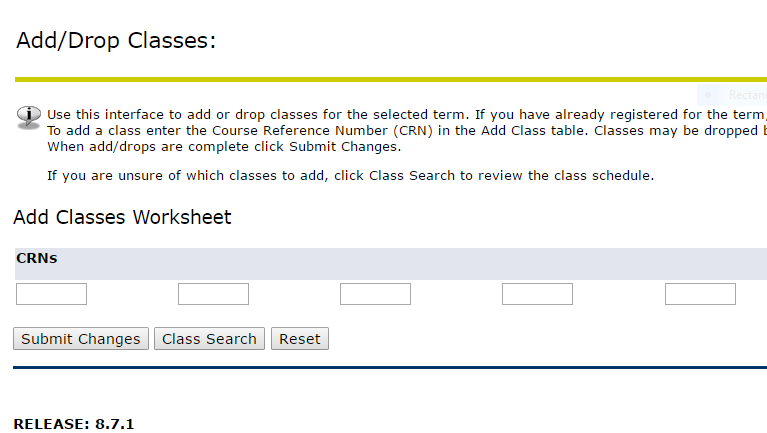
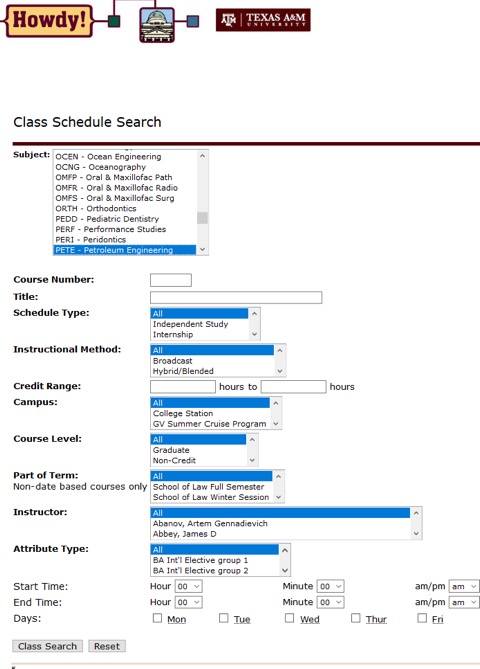
other examples?
usability
usability goals
effectiveness: effective to use
efficiency: efficient to use
safety: safe to use
utility: having good utility
learnability: easy to learn
memorability: easy to remember how to use
menus and keyboard shortcuts
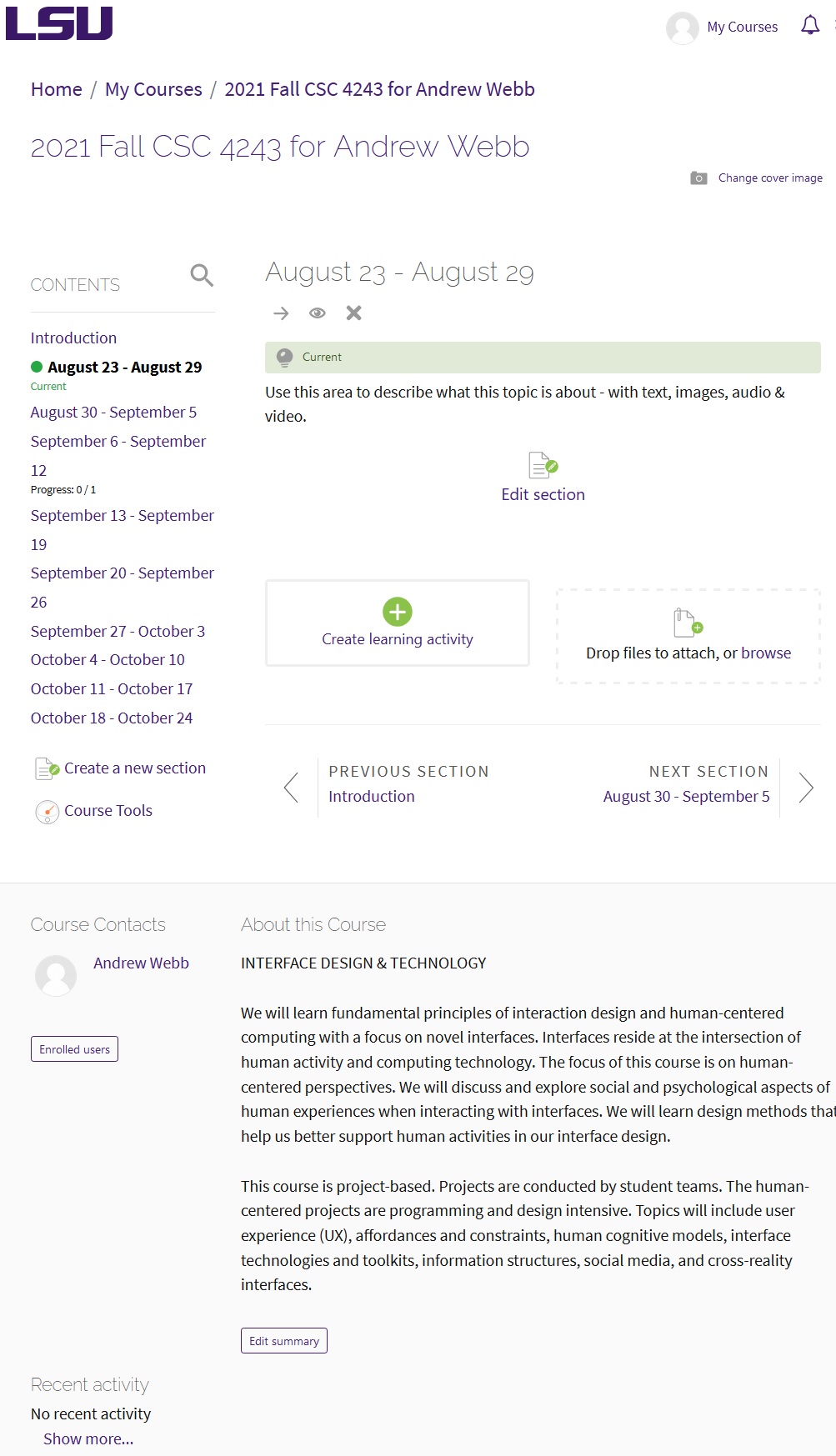
moodle
other examples?
accessibility and inclusiveness
accessibility
accessible to a wide audience by enabling
different ways of interacting
inclusive design of technology
design of assistive technology
types of impairments: sensory, physical, and cognitive
other examples?
design principles
visibility
make clear possible actions
feedback
response to action
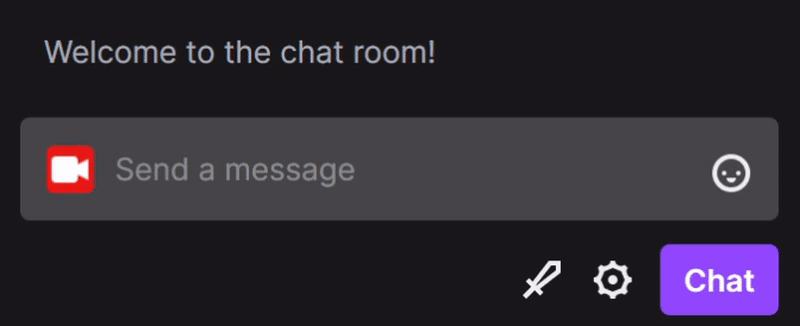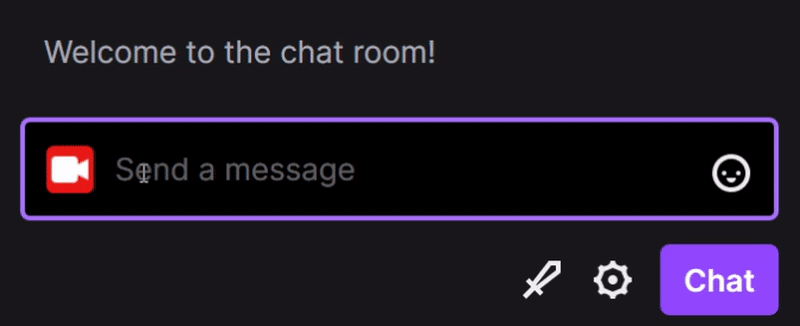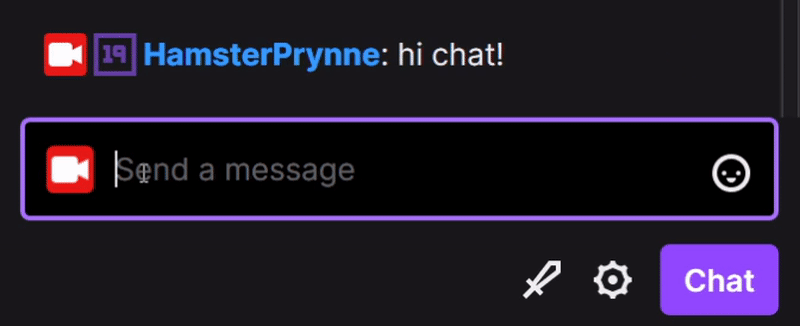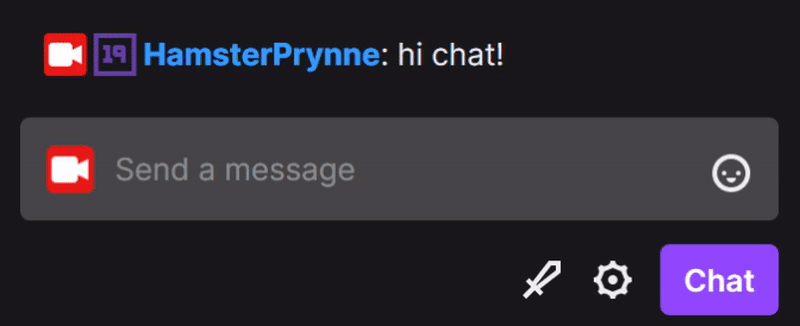
mapping
controls ↔ effects
example: pause on Twitch vs YouTube Live
consistency
similar elements for similar tasks
easier to learn and use
in-class activity
smartphone
consider a task you perform with your smartphone
questions
what is good and bad about the way it works for those tasks?
what in its design makes it work positively or negatively?
how does that relate to principles:
visibility, feedback, mapping, consistency?
user experience goals: satisfying, enjoyable, helpful, rewarding?
usability: effectivenes, efficiency, safety, utility, learnability, memorability?
what would you change? why would it be better?
show and tell
reading for next class
Chapter 1: "The Psychopathology of Everyday Things"
The Design of Everyday Things
